So this post is going to be about Bitcoin and the big plans to save us from Debt. The current mythology is Bitcoin was invented in 2008 by an unknown person or group of people using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto.
The invention was announced through a whitepaper titled "Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System,"which was published on October 31, 2008, on a cryptography mailing list. The whitepaper outlined the concept of a decentralized digital currency that operates without the need for a central authority or intermediary.
This was at the peak of the Great Financial (Banking) Crisis. Some coincidence.
On January 3, 2009, the first block, known as the genesis block , was mined by Satoshi Nakamoto. It contained 50 BtC. He would eventually own 1 million Bitcoin and stopped trading in 2010 never to be heard of again. His Bitcoin today is worth 105 billion. Imagine the tax on that?
Why would someone who invented Bitcoin not want to cash in on fame and collect their $100 billion which may soon become $1 trillion? Tis a mystery, and myths like mysteries.
So as we all know from 2009-2016 nobody in the real world paid much attention to Bitcoin except geeks, criminals and intelligence agencies, and those in countries with an unreliable or restrictive currency.
Up to 65% of the miners were in China and most of the Bitcoin being traded was outside the US or transnational (in or out of US) . It wasn’t yet an appreciating asset but that didn’t matter to those outside the US if their own currency was depreciating. Supposedly it was an anonymous way to move money around that was supplemented by Tor which was a way to communicate anonymously about trades or activities involving bitcoin transactions.
The early research on Tor was funded by the U.S. Department of Defense (DoD), specifically through the Office of Naval Research (ONR) and the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) with the research conducted at the Naval Research Laboratory
The goal of this research was to protect government communications and intelligence operations, not to create a tool for public use. It was released to the public because while adversaries could not know what was being communicated there were ways to detect it was being used and where it was being used which would expose intelligence agents if they were the only users, so public users served as a cover.
In 2004, the Naval Research Laboratory released the code for Tor under a free license. 4 years later comes Bitcoin.
After it was released to the public NSA then attempted to deanonymize it and likely succeeded. It is still being funded by the government.
The government as you know also built the internet starting with the DoD’ S ARPANET which then was handed off the the NSF and top Universities of the Military Academic Industrial Complex for further development as NSFNET before being gifted to private corporations to profit from
From Yasha Levines “Surveillance Valley “
The most important part of the system, the backbone, was run by a new nonprofit corporation, a consortium including IBM, MCI, and the state of Michigan. The second-tier regional networks were farmed out to a dozen other newly created private consortiums. With names like BARRNET, MIDNET, NYSERNET, WESTNET, and CERFNET, they were run by a mix of universities, research institutions, and military contractors.
NSF managers began the privatization process. “We told them: ‘You guys will eventually have to go out and find other customers. We don’t have enough money to support the regionals forever.’…. Telling NSFNET providers to diversify their client base by seeking commercial clients—it seems like a minor decision. Yet, it is a crucial detail that had a huge impact
Vinton Cerf, who in 1982 had left his job at ARPA to head up MCI’s networking division, described Wolff’s private-public network provider scheme as “brilliant.” He said, “The creation of those regional nets and the requirement that they become self-funding was the key to the evolution of the current Internet.”
The Internet is perhaps one of the most valuable public inventions of the twentieth century, and decisions made by a few key unelected officials in the federal bureaucracy set the Internet on the certain path to privatization. There was no real public debate, no discussion, no dissension, and no oversight. It was just given away, before anyone outside this bureaucratic bubble realized what was at stake.
Legally, NSFNET contractors were not allowed to route their commercial traffic through the government-funded network.
Later, the NSF managers claimed that NSFNET providers didn’t violate these terms and that they routed commercial traffic through separate, privately built network infrastructure. But a backroom deal the NSF made with its backbone operator shows that the truth is a bit murkier.
In 1990, the MCI-IBM consortium, with approval from NSF, split into two corporate entities: a nonprofit called Advanced Network Services and a for-profit confusingly named ANS CO+RE Systems. Advanced Network Services—ANS—continued to contract with the NSF to maintain and run the physical NSFNET backbone. Meanwhile, its for-profit division, ANS CO+RE, sold commercial network services to business clients on a new network it called the ANSNET.
Of course, this new ANSNET ran on the exact same physical network infrastructure that powered the NSFNET. Legally, though, the two—NSFNET and ANSNET—were treated as completely separate entities by the National Science Foundation, which meant that despite the Acceptable Use Policy that forbade commercial traffic on the NSFNET, the IBM-MCI consortium had a green light to do just that for profit. It was a clever maneuver.
On a basic level, it allowed the MCI-IBM consortium to double book the same asset, pocketing government money to run the NSFNET and then selling this same network to commercial clients. More fundamentally, it allowed a corporate entity with a direct stake in the business of computer networking to privatize a government asset without doing so explicitly.
“It’s like taking a Federal park and giving it to K Mart. It’s not right,” a manager of a large NSFNET provider told the New York Times.
The key to this advantage was the NSFNET backbone itself. Built and sustained with government funds, the network spanned the width of the United States and had connections to more than thirty other countries.
Regional networks, on the other hand, were smaller, usually restricted to geographic areas like Greater New York, the Midwest, or northern California. Those that expanded into the national commercial market could not route commercial traffic through the NSFNET backbone but had to build their own private networks without government funding. In short, the NSF directly subsidized the MCI-IBM consortium’s national business expansion. The company used its privileged position to attract commercial clients, telling them that its service was better and faster because it had direct access to the national high-speed backbone.
William Schrader, president of a New York area provider called PSINET, charged the NSF pointblank with granting a monopoly over government assets to a single privileged corporation. “The Government has privatized the ownership of a federal resource,” he said at a 1992 congressional hearing held to investigate possible government mismanagement of the NSFNET. “The privatization unnecessarily provided the contractor [IBM-MCI] with an exclusive monopoly position to use Federal resources paid by taxpayer funds.”
Schrader wasn’t contesting the privatization itself. Why would he? His own company, PSINET, had also been spun off from a regional NSFNET provider seeded with federal money as a for-profit entity. Like IBM-MCI’s ANS, PSINET represented a de facto privatization of a government-subsidized asset by a few privileged insiders who happened to be at the right place at the right time. Schrader didn’t challenge that. What he opposed was the NSF giving a different—and perhaps more powerful—group of privileged insiders more privilege than his company had received.
A few select companies had been providing ARPANET-like access to large corporations since the 1970s. But, in the late 1980s, all sorts of dial-up and networking services popped up across the country. There were big firms like CompuServe, Prodigy, and America Online as well as hundreds of smaller outfits.
This was not the globally connected Internet we know today. Services like The Well and America Online were not connected to one another and allowed communication only between members of the same service. Effectively, they were siloed, at least for a time.
Cable and phone companies pushed for privatization, as did Democrats and Republicans in Congress. “There was little public debate or opposition to the privatization of the NSFNET,”
In 1995, the National Science Foundation officially retired the NSFNET, handing control of the Internet to a handful of private network providers that it had created less than a decade earlier. There was no vote in Congress on the issue. There was no public referendum or discussion. It happened by bureaucratic decree
A year later, President Bill Clinton signed the Telecommunications Act of 1996, a law that deregulated the telecommunications industry, allowing for the first time since the New Deal nearly unlimited corporate cross-ownership of the media: cable companies, radio stations, film studios, newspapers, phone companies, television broadcasters, and, of course, Internet service providers. The law triggered massive consolidation, culminating in just a handful of vertically integrated companies owning the bulk of the American media market.
A handful of powerful telecommunications companies absorbed most of the privatized NSFNET providers that had been set up with funds from the National Science Foundation a decade earlier. San Francisco Bay Area’s regional provider became part of Verizon. Southern California’s, which was part-owned by the military contractor General Atomics, was absorbed by AT&T. New York’s became part of Cogent Communications, one of the largest backbone companies in the world. The backbone went to Time-Warner. And MCI, which had run the backbone along with IBM, merged with WorldCom, combining two of the biggest Internet service providers in the world.
All these mergers represented the corporate centralization of a powerful new telecommunications system that had been created by the military and ushered into commercial life by the National Science Foundation. To put it another way, the Internet was born.
Many of the largest Tech Companies today that are profiting off the internet were funded by government agencies like DARPA, In Q-Tel, etc and/or have lucrative government contracts (or contracts with government backed contractors) providing services and sharing information. Google, Facebook, Amazon, Microsoft, Palantir, Apple, Twitter, etc.
Bitcoin also deserves a big assist from Government, as I will explain here with the help of Deep Seek and Chat GBT, although no direct link with NSA has been found due to the fact we don’t know who created it.
What follows is from Deep Seek
Satoshi Nakamoto relied on and built upon earlier work by others in the fields of cryptography, computer science, and digital currencies. Bitcoin was not created in isolation; it was the culmination of decades of research and innovation by various pioneers. Here are some key influences and earlier works that contributed to Bitcoin's creation:
1. **Cryptographic Foundations**:
- **Public-Key Cryptography**:
- Bitcoin uses public-key cryptography to secure transactions. This technology was developed in the 1970s by **Whitfield Diffie**, **Martin Hellman**, and **Ralph Merkle**, and later formalized by **Rivest, Shamir, and Adleman (RSA)**.
The **RSA algorithm**, developed by **Rivest, Shamir, and Adleman**, was supported by government-funded research at MIT.
**Hash Functions**:
- Bitcoin relies on cryptographic hash functions (like SHA-256) for securing the blockchain. These were developed over many years by cryptographers, including **Merkle-Damgård constructions**.
The **SHA-256** hash function, was developed by the **NSA** and published by the **National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)** in 2001
2. **Digital Cash and Cryptocurrency Predecessors**:
- **David Chaum's DigiCash (1980s)**:
- David Chaum pioneered the concept of digital cash with his work on **blind signatures** and the creation of **DigiCash**, an early attempt at anonymous electronic payments.
- **Hashcash (1997)**:
- Created by **Adam Back**, Hashcash introduced the concept of **Proof of Work (PoW)** to combat email spam. Satoshi adapted this idea for Bitcoin's mining mechanism.
- **b-money (1998)**:
- Proposed by **Wei Dai**, b-money was a conceptual framework for a decentralized digital currency. Satoshi referenced Dai's work in the Bitcoin whitepaper.
- **Bit Gold (1998)**:
- Proposed by **Nick Szabo**,
Bit Gold was another early attempt at creating a decentralized digital currency. It introduced ideas like cryptographic puzzles and decentralized consensus, which influenced Bitcoin.
3. **Distributed Systems and Consensus Mechanisms**:
- **Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT)**:
- Research into Byzantine Fault Tolerance, which deals with achieving consensus in distributed systems despite faulty or malicious actors, was foundational for Bitcoin's consensus mechanism.
Based on work done in 1978 in the context of the NASA-sponsored SIFT project in the Computer Science Lab at SRI International
- **Peer-to-Peer Networks**:
- Bitcoin's peer-to-peer network design was influenced by earlier P2P systems like **Napster** and **Gnutella**, which demonstrated the feasibility of decentralized networks.
4. **Time-Stamping and Blockchain-Like Structures**:
- **Stuart Haber and W. Scott Stornetta (1991)**:
- Their work on cryptographic time-stamping and linking documents in a chain-like structure laid the groundwork for the blockchain concept.
5. **Economic and Game Theory**:
- Satoshi incorporated economic incentives and game theory into Bitcoin's design to ensure honest behavior by participants. This was influenced by earlier research in these fields.
Satoshi's Innovation:
While Satoshi built on these earlier ideas, the true innovation of Bitcoin was combining them into a cohesive, functional system that solved the **double-spending problem** without requiring a trusted third party.
This was achieved through the **blockchain**, **Proof of Work**, and a decentralized network of nodes.
In the Bitcoin whitepaper, Satoshi explicitly acknowledged the influence of **Hashcash** and **b-money**, demonstrating respect for the work of predecessors in the crypto space.
The 1996 NSA whitepaper titled **"How to Make a Mint: The Cryptography of Anonymous Electronic Cash"** is an interesting document that discusses the concept of anonymous digital cash and the cryptographic techniques required to implement it. While there is no direct evidence that **Satoshi Nakamoto** explicitly referenced this paper in the creation of Bitcoin, the ideas in the whitepaper align closely with some of the principles underlying Bitcoin and other cryptographic currencies.
Satoshi’s innovation was not in inventing new cryptographic techniques but in combining existing ideas (e.g., Proof of Work, decentralized consensus, and blockchain) into a functional and practical system
Some people including myself have suspected Wei Dai of being Satoshi. Here is what Chat GBT has to say
Wei Dai played a foundational role in the development of Bitcoin through his early work on cryptographic digital currencies and decentralized systems. Although he was not directly involved in the creation of Bitcoin, his ideas and innovations significantly influenced its design. Here’s a detailed look at Wei Dai’s contributions:
Wei Dai’s Contribution: B-Money
In 1998, Wei Dai proposed B-Money, a concept for a decentralized, digital currency. This proposal, published in a short white paper, outlined ideas that later became essential to Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies.
Key elements of B-Money include:
1. Decentralization• Wei Dai described a system where participants collectively maintain a ledger without relying on a central authority, similar to how Bitcoin operates today.
2. Proof-of-Work (PoW)• The B-Money proposal included the use of computational work to establish consensus, a precursor to Bitcoin’s Proof-of-Work mechanism. While not as fully developed as Bitcoin’s mining system, this idea laid the groundwork for decentralized consensus.
3. Anonymity• B-Money emphasized privacy and pseudonymity by allowing participants to interact using cryptographic identities, much like Bitcoin addresses.
4. Smart Contracts• Dai envisioned contracts enforced by the decentralized system, an early concept of smart contracts, which became a reality in later blockchain projects like Ethereum.
Influence on Bitcoin• Acknowledgment by Satoshi Nakamoto, Bitcoin’s pseudonymous creator, explicitly referenced Wei Dai and B-Money in the Bitcoin whitepaper (2008). Satoshi cited B-Money as an influence on Bitcoin’s design, alongside other key works like Nick Szabo’s Bit Gold.•
In the whitepaper, Satoshi noted that Bitcoin builds on B-Money’s ideas but provides a more complete implementation.•
Shared Concept Many of B-Money’s theoretical components, such as decentralized consensus, cryptographic identities, and PoW, were incorporated into Bitcoin, albeit in a more advanced and practical form.
Why Wei Dai Didn’t Create Bitcoin
Despite his contributions, Wei Dai never built a working implementation of B-Money. His work remained conceptual, and he expressed limited interest in developing a full system.
By the time Bitcoin was released in 2009, Dai seemed surprised by Satoshi’s success in solving the technical challenges he had outlined in B-Money.
Legacy
Wei Dai’s B-Money paper remains one of the foundational texts in cryptocurrency history, alongside works by Nick Szabo (Bit Gold) and Adam Back (Hashcash). Though Wei Dai didn’t directly contribute to Bitcoin’s code or development, his early vision helped shape the principles that underpin modern cryptocurrencies.
Deep Seek adds this
Professional Experience**:
- After completing his education, Wei Dai worked at **Microsoft** as a software engineer. While his work at Microsoft was not directly related to cryptography, the experience likely contributed to his technical skills and problem-solving abilities.
Wei Dai was part of the **cypherpunk movement**, a group of privacy advocates and technologists who promoted the use of cryptography to protect individual freedoms and privacy.
- The cypherpunk mailing list, where ideas about digital cash, anonymity, and cryptography were discussed, was a significant influence on Dai’s thinking. It was through this community that he became aware of concepts like **digital cash** and **anonymous transactions**.
Some other cypherpunks from Wikipedia
Marc Andreessen: co-founder of Netscape which invented SSL
Jacob Appelbaum: Former Tor Project employee, political advocate
Julian Assange: WikiLeaks founder, deniable cryptography inventor, journalist; co-author of Underground; author of Cypherpunks: Freedom and the Future of the Internet; member of the International Subversives. Assange has stated that he joined the list in late 1993 or early 1994.[7]An archive of his cypherpunks mailing list posts[55] is at the Mailing List Archives.
Hugh Daniel (deceased): former Sun Microsystems employee; manager of the FreeS/WAN project (an early and important freeware IPsec implementation)
John Gilmore*: Sun Microsystems' fifth employee; co-founder of the Cypherpunks and the Electronic Frontier Foundation; project leader for FreeS/WAN
Matt Thomlinson (phantom): security engineer, leader of Microsoft's security efforts on Windows, Azure and Trustworthy Computing, CISO at Electronic Arts
Satoshi Nakamoto: Pseudonym for the inventor(s) of Bitcoin.
Wei Dai: Created b-money; cryptocurrency system and co-proposed the VMAC message authentication algorithm. The smallest subunit of Ether, the wei, is named after him.
Zooko Wilcox-O'Hearn: DigiCashand MojoNation developer; founder of Zcash; co-designer of Tahoe-LAFS
Edward Snowden: NSA whistleblower (2013); President of The Freedom of the Press Foundation
Microsoft and the NSA**:
- **General Collaboration on Security**: Microsoft, as a major technology company, has worked with government agencies, including the NSA, on cybersecurity and encryption standards. For example:
- Microsoft has participated in government initiatives to improve cybersecurity and protect critical infrastructure.
- The NSA has provided input on cryptographic standards, which Microsoft and other companies implement in their products.
- **Controversies**: In the past, there have been controversies about Microsoft's cooperation with the NSA, particularly regarding surveillance programs like **PRISM**, revealed by Edward Snowden in 2013.
So could Wei Dai , Microsoft and NSA have collaborated on Bitcoin and collectively be Satoshi? This would explain why they need anonymity. After all, why would someone who invented Bitcoin not want to cash in on fame and collect their $100 billion which may soon become $1 trillion?
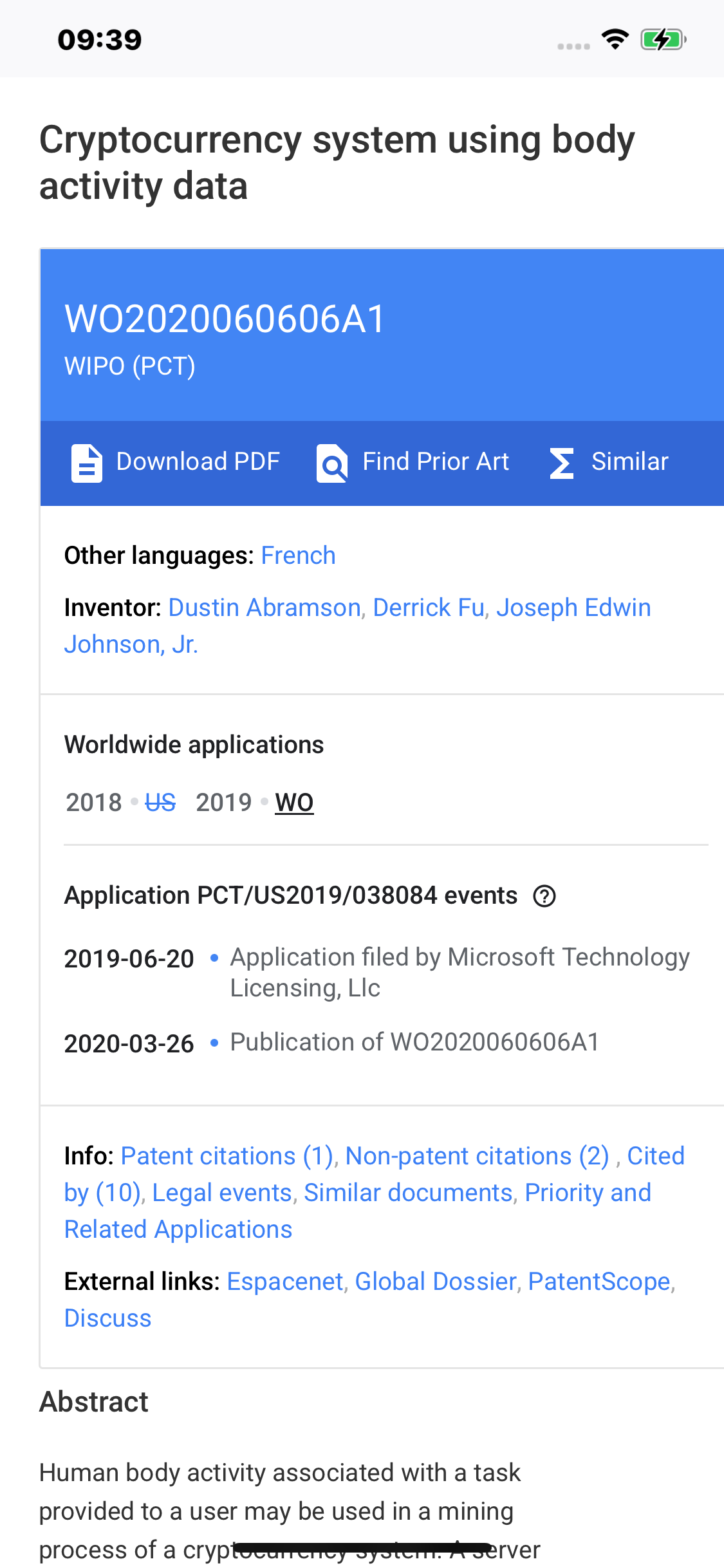
Just as an aside does anyone recall Microsofts creepy Crypto Patent 6*6*6*
Human body activity associated with a task provided to a user may be used in a mining process of a cryptocurrency system. A server may provide a task to a device of a user which is communicatively coupled to the server. A sensor communicatively coupled to or comprised in the device of the user may sense body activity of the user. Body activity data may be generated based on the sensed body activity of the user. The cryptocurrency system communicatively coupled to the device of the user may verify if the body activity data satisfies one or more conditions set by the cryptocurrency system, and award cryptocurrency to the user whose body activity data is verified.
Now some of you might know Mark Goodwin, he has been posting some good stuff at Whitney Webbs Unlimited Hangout.. Here is a fascinating extract of a transcript from his interview with Ryan Christian of TLAV. Its not in sequence and as such the context might suffer. Its a long interview but try to watch it in full if you can for full context. My comments are in italics
The US has a serious debt problem. It has $36 trillion in debt. We're at this point right now where the tax receipts are not nearly enough. We're not getting nearly enough money in from taxes. The interest rate on our debt, so you take out a big loan, You have to pay the interest that doesn't actually go against the principle. You're just paying to service the loan, right?
Mark doesn’t yet see that exaggerating the debt is part of the con. The US has $220 trillion * in assets (public and private) and we owe 36 trillion payable in our own currency which we can print.
Thats like having $2.2 million in assets and taking out a 360,000 mortgage when you have a printing press that can print the interest payment. Any banks going to approve that loan
Most of the recent debt is in short term treasuries which will be renewed at lower interest rates once the Fed lowers the rates. Congress can also allow the Fed to buy direct as the Fed must return the interest.
As for revenues being low thats a choice that can be eliminated with higher taxes on corporations and the rich like we had from the 40’s-70’s
* https://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/z1/20241212/z1.pdf
Chat GBT confirms
Yes, based on the figures provided in the Federal Reserve’s Z.1 Financial Accounts of the United States report, it would be reasonable to estimate the total assets of the U.S. (combining households, nonprofit organizations, the federal government, and state and local governments) as approximately $220 trillion.
Just servicing the debt that we have is actually greater than the money we spend on our defense now. And that's a very important axiom when we pass that point. So we're actually paying more to service the dollar than we are to pay for our military, which is supposed to sort of protect our dollar in this petrodollar system.
Um, so if we, uh, you know, demonetize gold, um, and, and, and an opportunity where normally, you know, we would be able to just say, Hey, a goal, an ounce of gold is $30,000. …..you know, we're holding billions of dollars of gold. Now we 10X it and we have enough money in gold.
We reset the price in dollars. We can pay off our debt tomorrow. We could do that 100%. But what would happen is every other country that holds gold would then be able to come to the United States and sell gold for 10X the price,
and they would be able to get out of all of their debt issues too. Exactly. So what's very interesting about the Bitcoin play is that the majority of it is in the United States already.
The U.S. Department of the Treasury records the nation’s gold reserves at a statutory value of $42.2222 per fine troy ounce, which gives us $11.5 billion. The market price is $730 billion. If we inflate the price of gold 10 x thats only 7.3 trillion. Not close to eliminating the debt.
There is some talk of resetting the price of gold held by the Treasury to market price and using the difference ($700 billion) to buy Bitcoin.
So what's very interesting about the Bitcoin play is that the majority of it is in the United States already.
I think Mark is wrong about this but I will discuss this later.
Significantly through these ties to early Bitcoin having this heavy, heavy tie to Silicon Valley, PayPal Mafia specifically, maybe even coming out of PayPal.
We'll get into that. But there's this ability for the US to basically reprice Bitcoin by buying up a ton of Bitcoin and sort of skipping that debt default
The thing about debt Is that if there were no debt there would be no money. The USD is a debt based currency. It’s created from loans. Each dollar represents a dollar of debt in some form. Eliminate $36 trillion in debt and you will eliminate $36 trillion in dollars. Great Depression on steroids. Furthermore, our debt is payable in dollars. If we have the equivalent of $36 trillion in Bitcoin and want to pay off the $36 trillion in debt we have to find someone who has $36 trillion dollars to pay. But our money supply is only $21.5 trillion. We could hand over $36 trillion Bitcoin Certificates to the Fed in exchange for $36 trillion dollars like we did with Gold. This is basically an iou representing our debt in Bitcoins. But then we got a problem, all those folks with Treasuries (30% of whom are foreigners) which cant be used to buy groceries or houses now have $36 trillion cash fresh off the printing press. Weimar Republic Inflation here we come
Trump [was] going on Twitter and going on this whole thing about, hey, I hate Bitcoin. It's trying to fight the dollar. You know, the dollar's king, blah, blah, blah. And everyone is like, oh, my goodness. And Bitcoin sells off and all this stuff. But in reality, you know, his team knew exactly what they were doing.
They set up, you know, basically what we're about to see now with him coming in, Bitcoin's at 100K. And we're seeing more regulatory push for, you know, direct action of the US government holding Bitcoin and, you know, all these things.
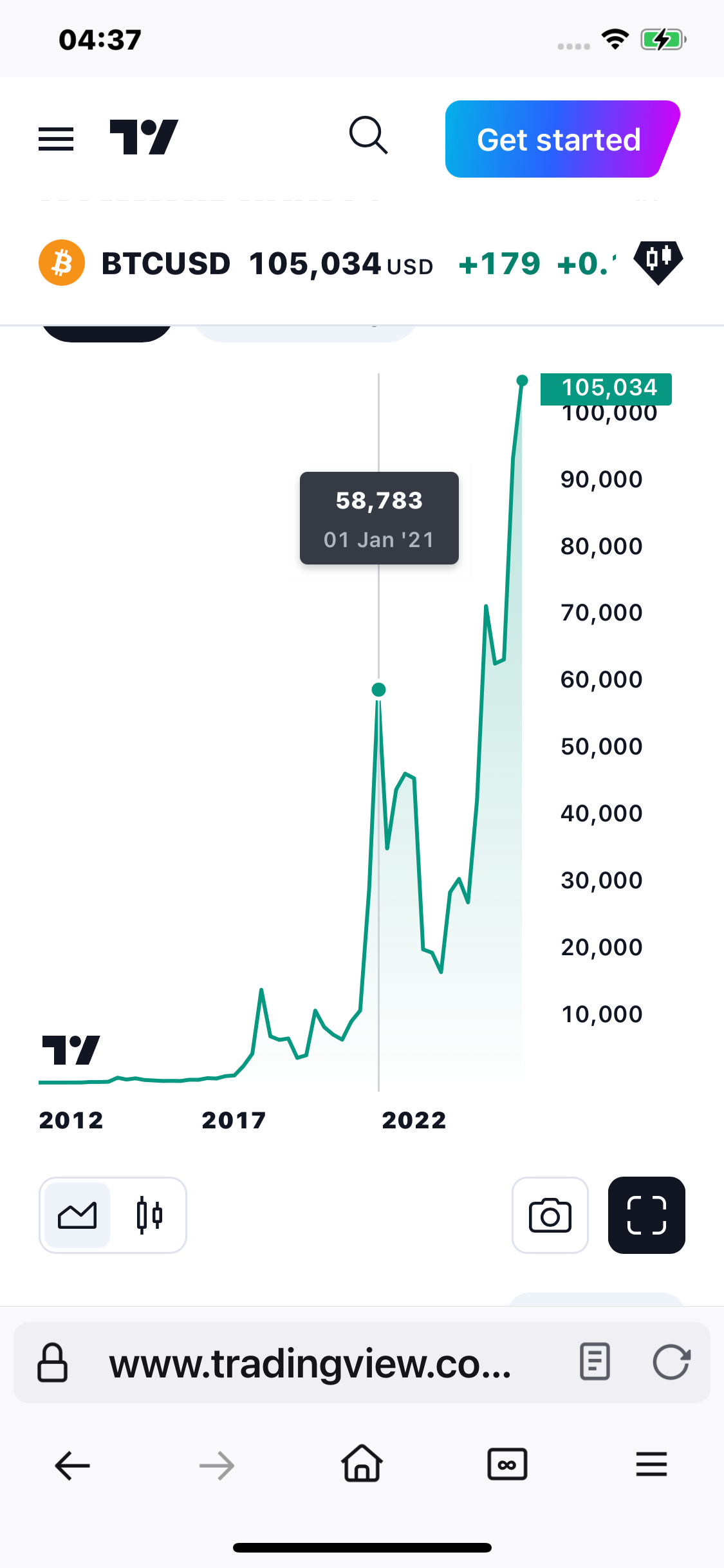
When Trump and RFK Jr announced setting up a Bitcoin Strategic Reserve in July Bitcoin was trading at $58,000, about what it was when he left office. Now its $105,000
But if you were really paying attention to his policy right before COVID actually happened, which of course he leaves, you know, right, you know, more or less right after A lot of the severe COVID policy starts and Biden comes in, becomes basically the fall guy.
Bitcoin was trading at around $1,000 when Trump took office it was about 58,000 when he left office, most of the gain coming when his Administrations OCC gave the Ok for banks to hold cryptocurrency in July 2020 and after Trump massively inflated the money supply by $5 trillion
And now Trump comes in as this rehabilitated hero who's saving America and using Bitcoin and literally says, I'm going to cut a little crypto check. and pay our $36 trillion in debt. If you were paying attention, he set this all up his first administration while tweeting about how he was doing the opposite. And that's what he does.
I think Trump is very obviously this sort of, you know, he's a Trojan horse kind of candidate himself, where people just sort of You know, ideologically, you're like, oh, that's my guy we got, you know, but then he's ushering in, I think, this technocracy at a rate faster than, you know, anyone has done in the past.
And he has created a narrative that these Bitcoiners that we're all about and the Fed are now literally saying, mend the Fed.
Let's fix the US debt problem with Bitcoin. Let's cheer that BlackRock is pumping our bags. And a lot of the – I think the ethos of the community was hijacked, but I don't think the protocol was.
I think that that deflationary, disinflationary monetary policy, it was supposed to become this asset, this neutral asset that we could use, that we could inflate the dollar into while we hold all the Bitcoin, and then we become the – Bitcoin winners of the world. And we basically extend our hegemon another 300 years, maybe even longer at the most important technological axiom crux, whatever moment in history as AI and, and all of these things are popping off.
It's like, I don't believe in multipolarity anymore, really, after COVID. I really think that it is. We are in a one world empire context, unfortunately. And I think the U.S. Silicon Valley tech oligarchs are that group. They run the Trump administration, frankly. I hope I can say that.
So the way that the Bitcoin system is set up right now is there are these things called stable coins that basically work as the liquid money market, the transactional money market for Bitcoin, for people to trade, for people to transact in. And so these stable coins, which are very importantly backed by U.S. debt, Treasuries, they are the fastest growing market for U.S. debt.
They are rapidly outpacing national buyers of U.S. debt in these things called T-bills, treasury bills, basically securitized debt that the U.S. government sells that backs dollars. Things like Tether now have $150 billion of debt. They've only been around for a few years.
They only crossed $10 billion of debt in 2020. Now they have 150 plus billion. For reference, China and Japan historically are two largest debtors or creditors rather. They have, you know, just under a trillion or sorry. Yeah, just under a trillion in debt. So already Tether, this tiny firm that has like 50 employees,
basically has over a tenth of the share of the largest nation state that holds our debt. Howard Lutnick, who's the incoming commerce secretary, owns a percentage of Tether. um and uh you know we're seeing you know a possibility basically that not only is bitcoin basically this trojan horse for uh the new petrodollar system we create
this bitcoin dollar system where rather than forcing people to buy dollars to buy oil we force them to buy dollars to use bitcoin tether is sort of i mean it's called tether i mean come on but tether is basically this this mechanism that allows the the petrodollar to evolve into the bitcoin dollar
They do have blacklist capabilities. The CIA, the Secret Service, private versions of the CIA, like Chain Analysis, which was funded by In-Q-Tel, which is the CIA's venture capital firm, are all onboarded onto Tether's system. So they can seize and surveil You know, these private issued government backed stable dollar stable coins that are on public blockchains. It's the worst of all worlds for us.
It is the CBDC. We are all so afraid of CBDC is coming from the government because why? Because we're afraid of programmability, surveillability and sees ability. Well, guess the fuck what? It's that, but worse because it's private entities. They don't have constitutional protection saying you can't do this to a person. They're private companies. They can do whatever they want. No shoes, no shirt, no service. They can do whatever they want.
So I think that there's this... sort of sly roundabout way that they've created this Bitcoin dollar system where if we don't push Bitcoin to allow it to be something that can service billions of people,
who does it actually service and who does it empower to bring this back to the top of the conversation? It empowers the US empire. And it has now become a way for us to service our Our meaning the US government, not that I really identify as a US government member, but hey, the US government is allowed to service their debt by the stable coins buying up all of these treasuries.
So if Bitcoin goes to be $100 trillion market, and then we have 10% of that, 20% of that being met in treasury demand from stable coin providers, because that's how you make it liquid. That's how you transact with Bitcoin.
There we go. We've got $20 trillion. We've basically solved our debt crisis by selling it to this one tech firm. Then you go to look at the tech firm, perfect transition into PayPal.
Then you get to look into the tether firm and you look at these people and they have incredible connections to the incoming Trump administration and the PayPal mafia.
I've been very wary of Peter Thiel and the PayPal mafia, but I hadn't really looked into early PayPal history. Um, and I read this book. I actually have it, uh, right here. I will show, um, This guy, Eric Jackson, he was an early marketing employee at PayPal, and he wrote this book called The PayPal Wars. That's a book that just explains kind of the foundation of the formation of PayPal. And in it, he talks about this meeting that he had as soon as he got hired. And Thiel calls the group together. There's like 20 of them at that point, you know.
And he calls the group together and he explains why PayPal, like what PayPal is going to do. And what he says is that we're going to establish this new world currency. And the way we're going to do it is we are going to allow people across the world using the internet and the digitalization of the dollar to give citizens of the world of other nation states, the ability to opt out of their national local currency, which is, you know, hyperinflating or having all of these issues, debanking issues, will allow them with an internet connection to have access to the US dollar system.
And we're going to give, it's going to be this altruistic, amazing thing. Well, we're going to, for the first time ever, give the citizens of the world financial freedom
And PayPal is the centralized system where they can seize your funds. And, you know, when you peel back a little bit more of the foundation of PayPal, Max Levchin did this very illuminating talk with Charlie Rose, where he says, when I was making PayPal, I worked with every three and four letter agency,and they were some of the most fruitful business partnerships I ever had.
Thiel was the real first investor of PayPal was Thiel himself from Thiel Capital taking I think it was like $100,000 from his currency speculating that he was doing at Stanford. Stanford, of course, was one of the members of this MDDS group, which was where the CIA and the NSA and DARPA were funding companies.
You know, they funded Paige and Bryn to start Google. And so Stanford was a part of this group. So, you know, all of this stuff is kind of kicking off and the digital asset space is really popping off.
And Brock comes out basically as one of the early Bitcoin evangelists and very quickly on comes up with this idea for creating other assets to exist on Bitcoin. Um, so he does this thing called master coin, which ends up developing into tether. Um, and him and a couple other guys, one of the guys, um, is Craig Sellers, who was sort of the CTO, the technician. Um, I generally think he's a pretty cool guy. I, I, I think he's okay. Um, I like his takes. He seems to sort of understand the stakes here. But some of the other guys in there, William Quigley, who was connected with Clearstone and some others, not, not, not so great.
And they ended up establishing Tether. So kind of even before Bitcoin is really monetized at all, you know, the first real pump of Bitcoin where it really kind of got monetized and people paid attention was in the 2013, 2014, which is right when Tether comes out and they, and they established the first dollar, you stable coin.
And it is actually literally runs on Bitcoin at first. It runs on this thing called the Omni layer. So within the blocks, there was such a little transactional output on Bitcoin. Cause no, there was, you know, 10,000 people using it that they were able to put other assets, you know, within the ledger basically of Bitcoin, they could store other assets in there. You can still do that. But it's harder because there's a lot more competition for block space. But at the time they were able to basically bootstrap a digital dollar and Right on Bitcoin itself. And this is a company that Brock Pierce starts. Again, I think Tether was another one of those.
It's an infamously hated business. where it is routinely, you know, made fun of for not having audits routinely, you know, being referred to as money for human traffickers and launderers and it's Chinese real estate paper. And, um, you know, they've never passed a formal audit and the wall street journal and, you know, just New York,
just everybody is always sort of attacking tether for saying that they're not legitimate and they're going to pop at any moment. Once they do, Bitcoin is going to collapse. And they've been supporting Bitcoin because every time Bitcoin goes down, they print a couple million dollars of Tether and pump the price of Bitcoin back up.
And that's been this gambit for a decade now, right? That Tether is going to implode. Once it does, Bitcoin implodes. But what actually happened? the largest primary dealer for the New York Fed, Cantor Fitzgerald, which was started, actually not started, but the most important person in the company's history who's run the company essentially the entire time, Howard Lutnick, the Income and Commerce Secretary, runs this primary dealer, Cantor Fitzgerald. They're the largest trader of US debt in the world. Well, in the US anyway. And it turns out that they're holding all of the paper behind tether.
And not only are they in the most legit place custody that they, that they could in the entire world, he owns a stake of the business. And now they're coming in with this amazing opportunity to basically, you know, get, any legal action that had been taken against them, or they can be basically re-domicized into the regulatory arm of the United States due to this political coziness with the incoming...
So they painted this incredible picture that Tether was this incredibly fraudulent operation, but now they're crucial and critical to the survival of the U.S. debt system
PayPal wanted to create a new world currency, they come out and say, you know, Bitcoin survived or successfully created a new world currency where we failed. That's a quote from David Sachs. Guess what?
He's the incoming AI and crypto czar for Donald Trump. He was the first product manager or – yeah, I think product manager of PayPal. COO, excuse me. Yeah, so he's now one of the most important people theoretically in the government for setting the policy here. For both crypto and artificial intelligence, by the way.
Trump is coming out there being like, you will never get a CBDC under me. And all the little seals are clapping in the front row being like, yeah, hell yeah. But what is he doing? He's pushing private bank-issued stablecoins, which, again, we've already covered, are just as programmable, surveillable, seizable,
and actually worse than if it was directly a government, arguably, because constitutional protections don't exist.
So we're seeing this total PayPal mafia takeover of the incoming government, and there's this weird sort of dynamic where... You know, the US intelligence, you know, community basically went into Silicon Valley and established the internet, established PayPal, Facebook, Google.
Um, now they're coming back to roost to Pennsylvania Avenue. And these people have billions, if not trillions of dollars of reasons to promote Bitcoin and Tether. Or what I think is really going to happen with stable coins is PayPal just released their own stable coin that was issued by this issuer, Paxos. It's a very interesting company. But they're going to do their own stablecoin.
So what I think is going to happen is we're going to see banks and these fintech firms, but really banks adopt stablecoins as the underlying currency of their whole financial system internally. So we're going to see Bank of America and Wells Fargo and JP Morgan, all of these banks have cryptocurrency plays here, right? They're all doing their own little private things, whether it's a fork of Ethereum or whatever, but all these banks are going to issue stable coins. We're going to see all these private banks come in and do stable coins. I think ultimately Tether probably won't be the biggest one, but they certainly set the standard and quite literally tethered Bitcoin to the US dollar system. And perhaps for Fatally so, not that Bitcoin will collapse, quite the opposite, but probably prevented in a lot of ways.
A lot of the social capital and just literal capital is now going into developing Bitcoin. Bitcoin based stable coins and how do we get dollar instruments on Bitcoin? And that's sort of just seen as the way to scale Bitcoin rather than scaling Bitcoin itself. So if they're successful in that operation, basically, then I think the US has found a way to pay off their debt, a way to create a CBDC in effect without creating a CBDC and dealing with that headache. And find a way basically to extend hedge fund while other countries scramble to buy up Bitcoin and infrastructure to, you know, mine Bitcoin and have some sort of say in the validation of transactions on the network.
David Sachs is the crypto and AI czar. It's interesting that they're combining them together, but really if you look at sort of the, the two pillars of the incoming technocracy, it really is AI and in digital currency and cryptocurrency. And I think one of the things that, you know, this sort of triangulates those two pillars is digital ID. And, you know, you go to look at, you know, well, what's Thiels involvement with a lot of this [Palantir] really is a very advanced AI system that is fed on the best data sources possible. And, you know, who created the first digital ID? Facebook. It really was. It, it, it basically was the sly roundabout Trojan horse way for us to create our own digital identity system. We created a profile. We put our picture up there. We tagged the fucking squares on the faces to train the LLMs. And, you know, we added the things that we like and, you know we tagged where we were and you know we we built the monster really ourselves.
um and and you know Thiel was obviously introduced i believe to zuckerberg through ron conway who was kind of the handler of like sean parker um who was the napster creator who was a big part of you know the file sharing revolution and …You know, I've written a decent amount about that about, you know, well, maybe file sharing was a way to also roundabout us to create bandwidth on the Internet so they could launder our surveillance because you could very easily if if there's a microphone in our computer recording everything we're doing. they're uploading it but we don't have any peer-to-peer uploads on our system and on our routers it'd be very easy to see but if we're all downloading and uploading and sharing all these you know streaming videos and there's massive amounts of content being sent around it's really hard to see the data being sent from our devices so perhaps you know maybe the system was established to create uh you know basically to launder surveillance data through the pipes of the internet right that's kind of a separate conversation but interesting to think about.
but the first identity systems online really was facebook and then you could argue google also with gmail and some things and then even paypal a little bit and when you look at you know how you sign into websites right it's like you can sign in with Uh, your Gmail, you can sign in with your Facebook. You can use your PayPal on all of these different websites to sign in. And so you start to look at the intersection between ID, uh, digital ID and, and, um, you know, surveillable financial systems and how we created that on, on the internet.
Um, you know, Thiel was really there at the beginning of all of these things, or certainly Stanford university was there at the beginning of all these things with, with, with, uh, the Google boys.
Um, And then you even go a little generation back, you know, the Sun Microsystems guys that really built Eric Schmidt came out of Sun Microsystems. But Sun Microsystems was, you know, they took the counter path to Microsoft. Microsoft was personal computing. Sun was networks. They were like, it's all going to be on networks. You're never going to process anything on your own computer. It's all about network switching. So we're going to go build out the modern internet. And then they did. And Andy Beckelstein, I think is his name, who was the founder of Sun.
Sun stands for Stanford University... I forget what the N is, but the son in microsystems is from Stanford University because it was from a research project that was created on campus. And he was the first person to fund the Google boys. So Thiel kind of doing all this stuff. at Stanford and is pulling all the best and brightest.
David Sachs wrote for the standard review for him and all that. And so he creates PayPal. And then what they find is that the main thing that you have to deal with when doing digital currency is all the fraud. It's just an incredible amount of fraud.
So him and Max Levchin, who is the founding CTO, And in my mind, a very possible Satoshi candidate. He's a very big cryptographer who spent his entire time at college in Illinois working on distributed networks. And literally, there's a quote that you pulled up earlier of... Thiel going to the beach and Anguilla basically saying, you know, I met Satoshi there.
And while at that conference, Levchin did a talk where he showed the math of creating an open, transparent financial system and that the way to do digital cash isn't transparent or sorry, isn't anonymous. It's transparent.
And then that was kind of what they did with with PayPal. Um, and so, you know, they are creating all of these anti-fraud algorithms, you know, the capture, you know, that you use to get on the websites or whatever that, that really came out of PayPal in a lot of ways.
It was certainly popularized for you via PayPal in 2004. They realized they have something really big there, and they created this anti-fraud algorithm that was named Igor that was named after this Russian antagonist who kept just kind of being like na-na-na-na-na-na to PayPal and stealing all this money. And so they created this whole system to keep one-upping him, and eventually they did, and they built this really incredible anti-fraud system.
So in 2004, they basically, you know, Thiel was like, hey, why don't we use this system to like go track down terrorists? And so he privatized basically this DARPA cutout, total information awareness. Yeah, sure.
And so Thiel basically created this panopticon basically in the private sector at the whim of the US intelligence community that now had basically a digital federal reserve with PayPal behind it. A big part of intelligence – And certainly why a lot of intelligence went out into the private sector is because funding is really hard to come by when you're doing black book operations. So that's why you see a lot of drug running and gun running, because that's a really easy way to get cash that's off the books. Bitcoin really fills that role in a very interesting way and digital currency fills that role in a really interesting way where you can pay people. Just like it's cool that I could pay you right now and no one could stop us and that's sweet and you could go pay it locally with something and there's literally no one that could stop you. an intelligence broker could, you know, buy a cache of data on a, on like Etsy or something of like the people that are buying things on Etsy. And then, you know, they have a whole cache of users and they can feed it into an air, whatever, you know, Bitcoin, you know, works that way as, as a black book money also.
But ironically, Bitcoin is transparency technology. Every single, there's no encryption in Bitcoin. Ironically, everything is open. You can see every transaction on the blockchain forever, every single transaction that's ever been made on Bitcoin. I have a copy on my node right over there, every single one. So I think there's a great use case for.
Well, let me say one more thing. I have every transaction on node over there on a hard drive. But it's useless to me because I don't have intelligence level analysis capabilities of being able to triangulate using other data of IP addresses and other things. People posting on social media being like, I bought Bitcoin today.
And then you go and you look at when and then you say, OK, they bought this much. And so when combined, when this transparency technology is combined with Bitcoin, a program like Palantir, every single transaction that gets made on Bitcoin, 99.999% is able to be parsed by these chain analysis companies.
In-Q-Tel, which was a founder or funder of Palantir, also funded chain analysis. which is a data analytics firm for blockchains, if you don't have basically nation state level analytics of the blockchain, it doesn't necessarily mean much to you. I can't really do anything with the blockchain.
I can look at some things through a block explorer and look up Ukraine donations from FTX. I can look at some things, but I need to know a lot about the the data um that's given to me by other sources um i there's no way that i can really triangulate um you know who was sending it initially and all these things but a group like palantir and a group like um you know t you know like just government intelligence chain analysis they really can do a lot of damage with bitcoin um at the isp level so
So Bitcoin being a transparent technology, when combined with AI that can parse all of this stuff, and when combined with data brokers like Palantir that have huge caches of information on not just American citizens, but the world, your privacy is nil to none on Bitcoin. There obviously are a lot of people working on stuff.
Interesting stuff. I like the way he ties AI, Pay Pal Mafia, Silicon Valley, Palantir and Intelligence Agencies into the Bitcoin narrative. You can see how its all an interconnected BLOB united by a common purpose, which is probably not in our best interests.
I just noticed Tether invested $200 million in Blackrock Neurotech, a maker of brain-computer interface technology. Imagine a future with stable coins programmed to not transact if their users whose brain is connected to Neurotech or Neurolink is found to be thinking forbidden thoughts😳
Anyways, after all that its my belief that the Debt is only an excuse for the government to buy Bitcoin with the ultimate goal of eliminating the dollar as we know it and to get everyone on private banks stable coins which will be backed by the Digital Gold known as Bitcoin.
Every bank will accept the other banks stable coin, as will retailers. This was common before the Fed when chartered national banks could issue their own currency. It wasn’t phased out until the 1930’s
https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/National_Bank_Note
The Bitcoin backed USD will still be the World Reserve Currency even if it wont be used much for daily transactions in the US because Bitcoin is already in every country . Banks in the *Eurodollar market will still maintain dollar deposits for the rich who don’t want programmed money.
*Eurodollars are not Euros but USD used outside the US. These foreign banks accept USD deposits and then create their own digital USD via loans. Long but interesting story.
Mark seems to think most of Bitcoin is in the US , and maybe it is but I don’t see any sources supporting this.
But who knows, maybe the users in other countries just have smaller holdings
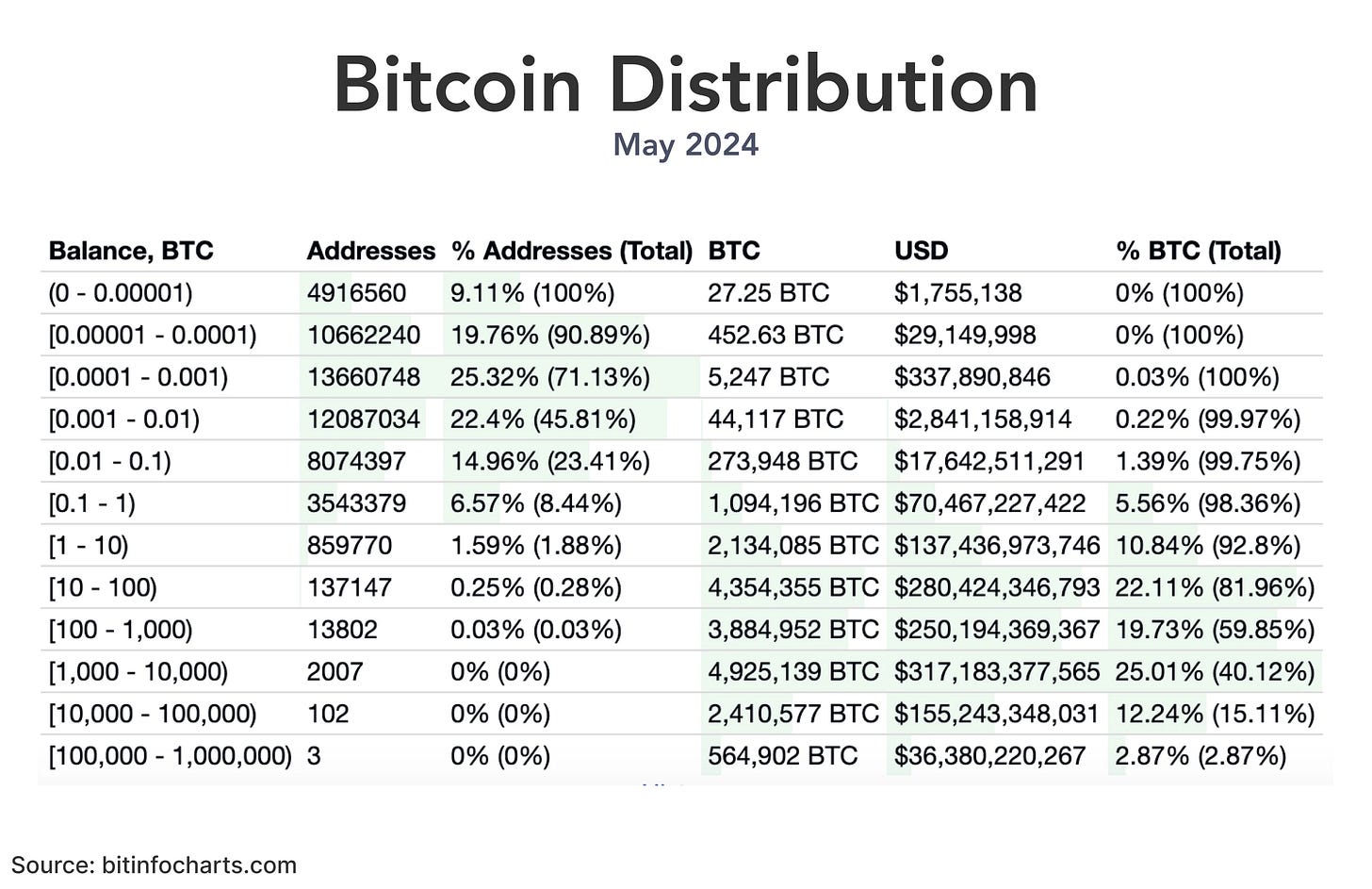
But 80% of Bitcoin is in only 150,000 addresses so its basically not going to equalize the distribution in wealth
I checked out Chat GBT and Deep Seek on Chinas Influence on Bitcoin
Chat GBT
As of September 2024, Chinese mining pools were responsible for approximately 55% of the global Bitcoin hashrate
Following China’s 2021 ban on cryptocurrency mining, several Chinese companies relocated operations to the United States. Reports have identified Chinese-owned Bitcoin mining facilities in multiple U.S. states, including Texas and Wyoming. These developments have raised national security concerns among U.S. officials.
If a single pool controls over 51% of the network’s hashrate, it could theoretically execute a “51% attack.”
Bitcoin mining chips are primarily produced by two major manufacturers:• Bitmain (China-based): One of the largest manufacturers of ASIC (Application-Specific Integrated Circuit) miners, used for Bitcoin mining.• MicroBT (China-based): Another key player in producing ASIC mining hardware.
While the specific percentage of chips made in China may vary, estimates suggest that over 70% of the ASIC chips for Bitcoin mining are manufactured in China, primarily due to the dominance of companies like Bitmain and MicroBT.
Deep Seek
Before the ban, China accounted for **65-75% of the global Bitcoin hash rate**, making it the world's largest Bitcoin mining hub.
While exact numbers are unavailable, industry experts estimate that **20-30% of Chinese miners successfully relocated** their operations overseas.
By late 2021, the U.S. had become the largest Bitcoin mining hub, accounting for over **35% of the global hash rate**, while China's share dropped to near zero.
Chinese mining pools were responsible for approximately 55% of the global Bitcoin hashrate
and
If a single pool controls over 51% of the network’s hashrate, it could theoretically execute a “51% attack
That concerns me. If the Chinese pools can act in a collective manner they can launch an attack. WTF are we talking about Tik Tok for.
While Mining Bitcoin is illegal in China since 2021 owning Bitcoin is not illegal in China so we basically have no idea how much Bitcoin is owned by Chinese Citizens, government or Corporation inside or outside of China.
Chinas 2021 action was very interesting in itself. If you follow me you may know I have contended that China is a Fake Wrestling partner. Their pushing out their miners opened the door to the idea of a US Bitcoin Strategic Reserve to free us from debt since there is no way it could be sold with 65% of the miners hash rate in China.
My guess is each country will confiscate their citizens Bitcoin like FDR did with Americans Gold. This is done by making it illegal to own Bitcoin and shutting down all the exchanges. So if you own Bitcoin you get 1 chance to come clean and turn in your asset worth $1 million per Bitcoin or more. Who’s going to pass that up if it means risking jail time and asset forfeiture by refusing to do so
Also, since Bitcoins main value now is as an asset and not for transactions it seems silly for their supporters to maintain the need for anonymity. It should be a simple matter for governments to legislate that all Bitcoin users register their identity under penalty of confiscation.
https://www.schneier.com/blog/archives/2022/04/de-anonymizing-bitcoin.html
After the governments confiscate all the Bitcoin their citizens own they use it to back their CBDC or programmable stable coin currencies. In the US case this will be issued by private banks. You can choose in the beginning but eventually all banks will converge on a uniform programmable stable coin and the only difference will be its name.
Basically just a sneaky way of rolling out CBDC which is associated with slavery by using something associated with freedom. Truly Orwellian.
Conclusion- Bitcoin seems to be a Trojan Horse dressed up as Freedom and Debt Relief to promote private bank stable coins doing the same thing as a CBDC, which will then be used to enslave us.