Interesting Recent COVID Papers
This isn’t for everyone. If you don’t like to read technical papers, you might not want to bother.
Lets start with those related to Children since FDA is preparing to feed Moloch some younger kids by issuing some more EUA’s.
CHILDREN’S STUDIES
Severe acute hepatitis in children: investigate SARS-CoV-2 superantigens
(Keep in mind the vaccine produces sime of the same antigens)
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2468125322001662#!
Acute severe hepatitis of unknown aetiology in children: a new non-A-E hepatitis virus on horizon?
https://www.clinicalmicrobiologyandinfection.com/article/S1198-743X(22)00257-9/fulltext
Association of Prior BNT162b2 COVID-19 Vaccination With Symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Children and Adolescents During Omicron Predominance
In a test-negative, case-control study conducted from December 2021 to February 2022 during Omicron variant predominance that included 121 952 tests from sites across the US, estimated vaccine effectiveness against symptomatic infection for children 5 to 11 years of age was 60.1% 2 to 4 weeks after dose 2 and 28.9% during month 2 after dose 2. Among adolescents 12 to 15 years of age, estimated vaccine effectiveness was 59.5% 2 to 4 weeks after dose 2 and 16.6% during month 2; estimated booster dose effectiveness in adolescents 2 to 6.5 weeks after the booster was 71.1%.
Estimated vaccine effectiveness against symptomatic infection for children 5 to 11 years of age was 60.1% 2 to 4 weeks after dose 2 and 28.9% during month 2 after dose 2.
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2792524
Airways Expression of SARS-CoV-2 Receptor, ACE2, and TMPRSS2 Is Lower in Children Than Adults
Children were found to have significantly lower expression of COVID-19 receptors in the upper and lower airways (nasal and bronchial)
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32537478/
Nasal ACE2 Levels and COVID-19 in Children
Among a cohort of 305 patients aged 4 to 60 years, older children (10-17 years old; n = 185), young adults (18-24 years old; n = 46), and adults (≥25 years old; n = 29) all had higher expression of ACE2 in the nasal epithelium compared with younger children (4-9 years old; n = 45), and ACE2 expression was higher with each subsequent age group after adjusting for sex and asthma.
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2766522
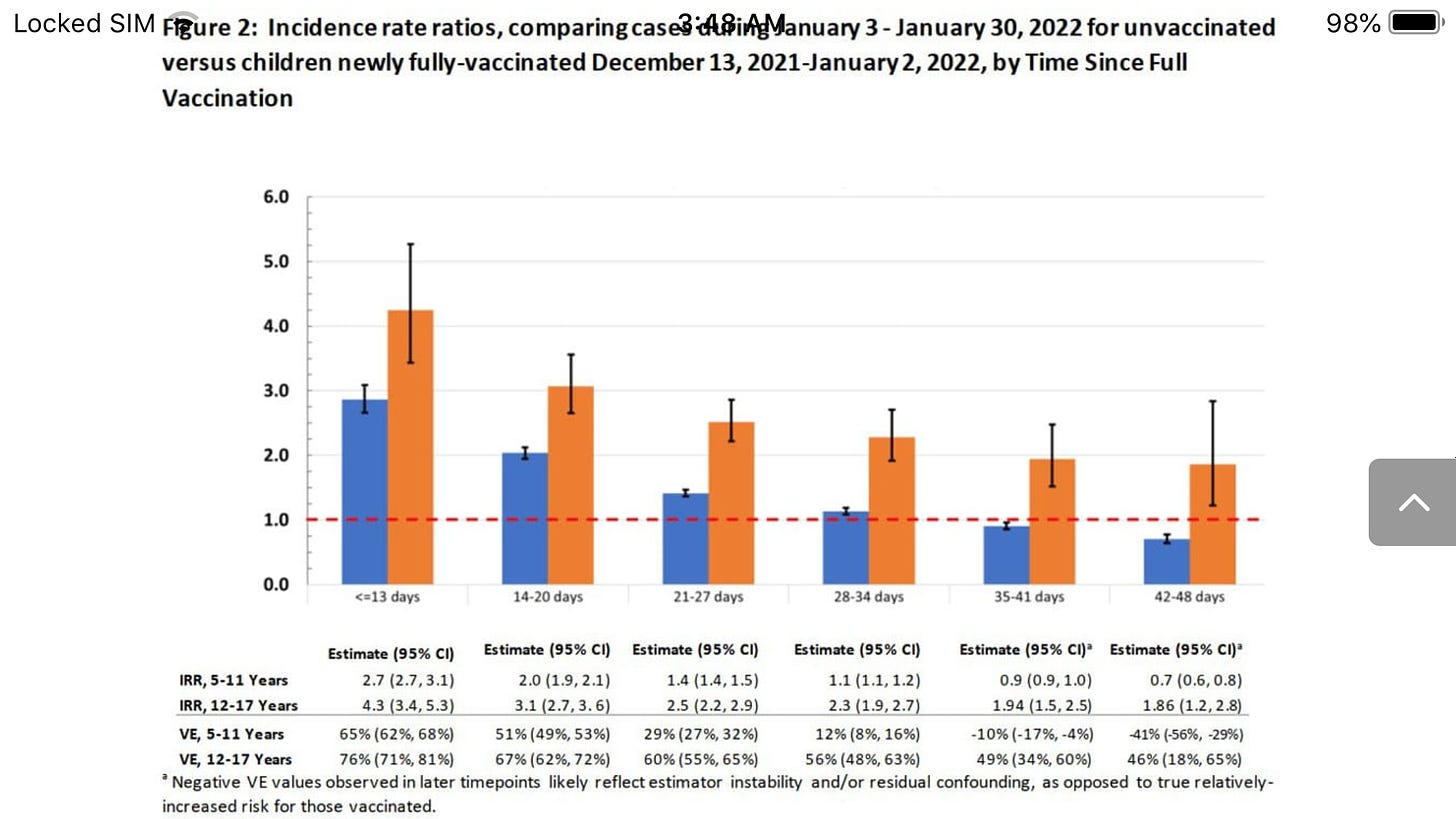
Effectiveness of the BNT162b2 vaccine among children 5-11 and 12-17 years in New York after the Emergence of the Omicron Variant
Examining time-since-vaccination, ≤13 days of full-vaccination, 12-17 years IRR was 4.3 (95% CI: 3.4, 5.3; VE: 76% [95% CI: 71%, 81%]), but by 28-34 days it was 2.3 (95% CI: 1.9, 2.7; VE: 56% [95% CI: 48%, 63%], Figure 2). For children 5-11 years,IRR at ≤13 days was 2.9 (95% CI 2.7, 3.1; VE: 65% [95% CI: 62%, 68%]) and at 28-34 days it was 1.1 (95% CI: 1.1, 1.2; VE: 12% [95% CI: 8%, 16%]).
For children 5-11 years,at 28-34 days after full vaccination the VE was 12%
Moreover, for young children (aged five to eleven), they observed a drop from 65 percent to just 12 percent after only one month.
Thereafter, their estimate indicated significantly negative effectiveness for this age group, as shown in Figure 2 of their paper: by 35 to 41 days, VE reached negative 10 percent, and by 42 to 48 days, it reached negative 41 percent.
https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.02.25.22271454v1.full.pdf
Estimated vaccine effectiveness against symptomatic infection for children 5 to 11 years of age was 60.1% 2 to 4 weeks after dose 2 and 28.9% during month 2 after dose 2.
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2792524
Evaluation of mRNA-1273 Covid-19 Vaccine in Children 6 to 11 Years of Age
https://www.nejm.org/doi/10.1056/NEJMoa2203315?url_ver=Z39.88-2003&rfr_id=ori:rid:crossref.org&rfr_dat=cr_pub%20%200pubmed
https://www.nejm.org/doi/suppl/10.1056/NEJMoa2203315/suppl_file/nejmoa2203315_appendix.pdf
Inhaled CO2 concentration while wearing face masks: a pilot study using capnography
The mean CO2 concentration was 4965±1047 ppm with surgical masks, and 9396±2254 ppm with FFP2 respirators. The proportion of the sample showing a CO2 concentration higher than the 5000 ppm acceptable exposure threshold recommended for workers was 40.2% while wearing surgical masks, 99.0% while wearing FFP2 respirators. The mean blood oxygen saturation remained >96%, and the mean end-tidal CO2 <33 mmHg
Among the minors, the mean CO2 concentration when wearing surgical masks was 6439±1366 ppm (5462 to 7415 ppm), and was considerably higher than among the adults (4852±857 ppm; p<0.001), or the elderly (4638±948 ppm; p<0.01). A
Lastly, the experimental conditions, with participants at complete rest and in a constantly ventilated room, were far from those experienced by workers and students during a typical day, normally spent in rooms shared with other people or doing some degree of physical activity. Since it was observed that speech and even low level physical activity are associated with increases in CO2 concentration, CO2 values in real life are likely to be higher than those recorded in this study
Concerning the risk of hypoxia, a research on 53 surgeons found that blood oxygen saturation decreased noticeably with a longer time wearing surgical masks.(29) In contrast, the present study was performed at rest and for a short time, during which the recorded levels of CO2 did not substantially alter blood oxygen saturation, as in similar studies.(9, 10, 30) Nevertheless, the exposure to inhaled air CO2 values higher than 5000 ppm, for long periods, is considered unacceptable for the workers, and is forbidden in several countries,(18) because it frequently causes signs and symptoms such as headache, nausea, drowsiness, rhinitis, and reduced cognitive performance.(31, 32) A
https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.05.10.22274813v1
Association of Prior BNT162b2 COVID-19 Vaccination With Symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Children and Adolescents During Omicron Predominance
Estimated vaccine effectiveness against symptomatic infection for children 5 to 11 years of age was 60.1% 2 to 4 weeks after dose 2 and 28.9% during month 2 after dose 2
5-22
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2792524
Validity of reported post-acute health outcomes in children with SARS-CoV-2 infection: a systematic review
https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.03.18.22272582v1
ADULT STUDIES
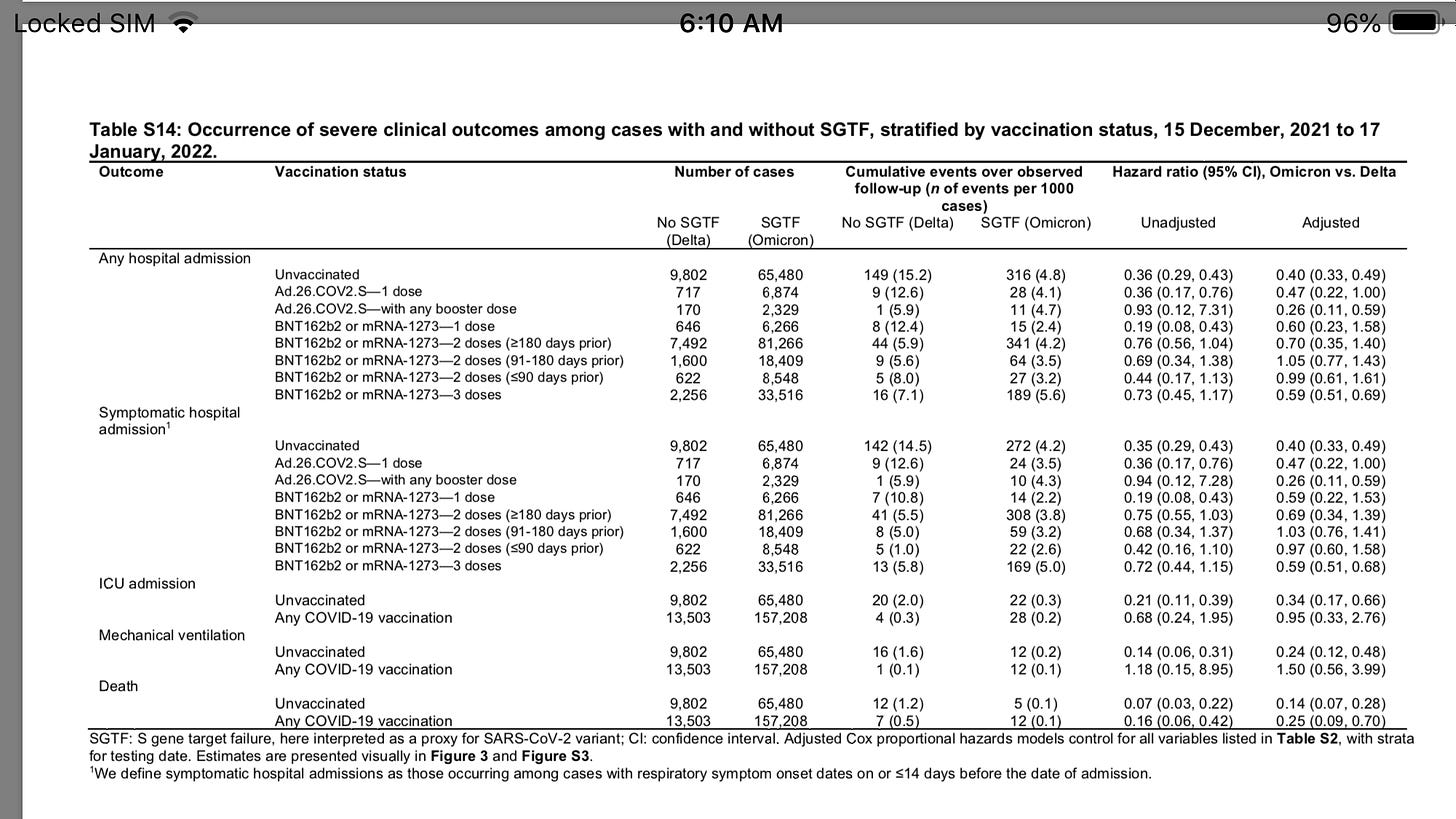
Study shows higher death from Omicron in vaccinated than unvaxxed (buried in supplementary tables)
Adjusted hazard ratios (aHRs) for any hospital admission, symptomatic hospital admission, intensive care unit admission, mechanical ventilation, and death comparing cases with Omicron versus Delta variant infection were 0.59 (95% confidence interval: 0.51-0.69), 0.59 (0.51-0.68), 0.50 (0.29-0.87), 0.36 (0.18-0.72), and 0.21 (0.10-0.44) respectively.
This reduced severity could not be explained by differential history of prior infection among cases with Omicron or Delta variant infection, and was starkest among cases not previously vaccinated against COVID-19(aHR=0.40 [0.33-0.49] for any hospital admission and 0.14 [0.07-0.28] for death).
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41591-022-01887-z_reference.pdf
Deaths higher in Vaccinated
Towards the emergence of a new form of the neurodegenerative Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: Twenty six cases of CJD declared a few days after a COVID-19 “vaccine” Jab
Luc Montagniers last paper published post-humously
Adverse effects of COVID-19 mRNA vaccines: the spike hypothesis.
Although rare, AEs include serious clinical manifestations such as acute myocardial infarction, Bell’s palsy, cerebral venous sinus thrombosis, Guillain–Barré syndrome, myocarditis/ pericarditis (mostly in younger ages), pulmonary embolism, stroke, thrombosis with thrombocyto- penia syndrome, lymphadenopathy, appendicitis, herpes zoster reactivation, neurological compli cations, and autoimmunity (e.g., autoimmune hepatitis and autoimmune peripheral neuropathies )....vaccine-induced AEs (e.g., myocardial infarction, Guillain–Barré syndrome) were found to increase with age, while others (e.g., myocarditis, anaphylaxis, appendicitis) were more common in younger people.
Although myocarditis cases are rather rare, in a study of US military personnel the number was higher than expected among males after a second vaccine dose ; similarly, the rate of postvaccination cardiac AEs was higher in young boys following the second dose .
Finally, a recent study showed an increased risk of neurological complications in COVID-19 vaccine recipients (which was nevertheless lower than the risk in COVID-19 patients).
The molecular basis of these AEs remains largely unknown.
We postulate that, since most (if not all) of them are also apparent in severe COVID-19 , they may be related to acute inflammation caused by both the virus and the vaccine, as well as in the common denominator between the virus and the vaccine, namely, the SARS-CoV-2 S protein .
The vaccine-encoded antigen (S protein) is stabilized in its prefusion form in the BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273 vaccines ; it is therefore plausible that, if entering the circulation and distributing systemically throughout the human body , it can contribute to these AEs in susceptible individuals.
Although chemical modifications in the RNA molecules used in vaccines (detailed earlier) are intended to decrease TLR sensing of external single-stranded RNAs (and thus proinflammatory signals), there is some evidence that modified uracil residues do not completely abrogate TLR detection of the mRNA; also, while efforts are made to reduce double-stranded (ds) RNA produc- tion, there may be small amounts of dsRNA that can occasionally get packaged within mRNA vaccines
Worth mentioning is a systems vaccinology approach (31 individuals) of the BNT162b2 vaccine (two doses) effects, where anticytokine antibodies were largely absent or were found at low levels (contrary to findings in acute COVID-19 [61,62]), while two individuals had anti-interleukin-21 (IL-21) autoantibodies, and two other individuals had anti-IL-1 antibodies . In this context, anti-idiotypic antibodies can be particularly enhanced after frequent boosting doses that trigger very high titers of immunoglobulins.
Frequent boosting doses may also become a suboptimal approach as they can imprint serological responses toward the ancestral Wuhan-Hu-1 S protein, minimizing protection against novel viral S variants
https://www.cell.com/action/showPdf?pii=S1471-4914%2822%2900103-4
Omicron lungs
In summary, our findings reveal that Omicron has faster and enhanced viral replication efficiency in the human bronchi compared with the previous lineages, suggesting that it has an intrinsic capac- ity for enhanced transmission. The lower replication competence of Omicron in human lungs is compatible with lower disease severity compared with Delta. Both of these observations are concordant with epidemiological data. Even if disease severity is modestly reduced, the very efficient transmissibility of Omicron will pose a major threat to global public health and health care systems. Investigations on prevent- ing Omicron infection through vaccination boosters and therapeutic options are urgently needed.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-022-04479-6
High viral loads: what drives fatal cases of COVID-19 in vaccinees? – an autopsy study
Median time between vaccination and the first positive PCR test was 10 days (range: 1–24). Eleven patients received the BNT162b2 vaccine (BioNTech), and four were vaccinated with AZD1222 (AstraZe- neca).
This study comprised 13 fully vaccinated cases. The median time from the last vaccination to a positive test of SARS-CoV-2 was 140 days (range: 28–283).
However, a high rate of viral dissemination detected by RT-qPCR within the organ system was an unanticipated result in this study, which was especially accentuated in the partially vaccinated compared to fully vaccinated cases (11 of 16 vs. five of 13, respectively; P = 0.144). In several cases, RT-qPCR identified the RNA of SARS-CoV-2 in all investigated samples, including cerebrospinal fluid, CNS, and soft tissues. This is in strong contrast to a previously published collection of the Augsburg series of nonvaccinated lethal SARS- CoV-2 infections, in which the frequency of viral dissemination was rare, with a rate of only 16% (three of 19)17 instead of 69%
According to the WHO classification, all but one patient died due to COVID-19.
Nucleocapsid (n) antibody testing was available for only 3 of the single dosed and for 11 of the double, but, provocatively, was detectable in ALL single dosed but only 45% of double dosed.
This finds strong alignment with other studies showing the inhibited inability of the vaccinated to produce N antibodiesa fact known (but only lately released) from the initial studies.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41379-022-01069-9.pdf
Protection and Waning of Natural and Hybrid Immunity to SARS-CoV-2
Based on date when Delta prevalent
The number of cases of SARS-CoV-2 infection per 100,000 person-days at risk (adjusted rate) increased with the time that had elapsed since vaccination with BNT162b2 or since previous infection.
Among unvaccinated persons who had recovered from infection, this rate increased from 10.5 among those who had been infected 4 to less than 6 months previously to 30.2 among those who had been infected 1 year or more previously.
Among persons who had received a single dose of vaccine after previous infection, the adjusted rate was low (3.7) among those who had been vaccinated less than 2 months previously but increased to 11.6 among those who had been vaccinated at least 6 months previously.
Among previously uninfected persons who had received two doses of vaccine, the adjusted rate increased from 21.1 among those who had been vaccinated less than 2 months previously to 88.9 among those who had been vaccinated at least 6 months previously.
https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa2118946
Viral nucleoprotein antibodies activate TRIM21 and induce T cell immunity
Nucleoprotein (N) is an immunodominant antigen in many enveloped virus infections. While the diagnostic value of anti‐N antibodies is clear, their role in immunity is not. This is because while they are non‐neutralising, they somehow clear infection by coronavirus, influenza and LCMV in vivo. Here, we show that anti‐N immune protection is mediated by the cytosolic Fc receptor and E3 ubiquitin ligase TRIM21
TRIM21 uses anti‐N antibodies to target N for cytosolic degradation and generate cytotoxic T cells (CTLs) against N peptide. These CTLs rapidly eliminate N‐peptide‐displaying cells and drive efficient viral clearance. These results reveal a new mechanism of immune synergy between antibodies and T cells and highlights N as an important vaccine target.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7917548/
Receipt of mRNA Covid-19 Vaccines and Risk of Spontaneous Abortion
In the sensitivity analysis, under the extreme assumption that all 65 participants (lost to follow up) with most recent contact during the first trimester had a spontaneous abortion, the cumulative risk of spontaneous abortion from 6 to less than 20 weeks of gestation was 18.8% (95% CI, 16.6 to 20.9); after age standardization, the cumulative risk was 18.5% (95% CI, 16.1 to 20.8).
About 10–15% of all natural pregnancies end in recognized spontaneous abortions ( Wilcox et al ., 1981 ; Risch et al ., 1988 ; Nybo Andersen et al ., 2000 ; De La Rochebrochard and Thonneau, 2002)
The study claimed 11-22%
https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMc2113891
Neuropathic symptoms with SARS-CoV-2 vaccination
In all three, symptoms improved dramatically within 2 weeks of IVIg treatment with complete resolution in one and mild residual symptoms in the other two
One of the two (Brianne Dressen)describes here mild residual symptoms and still is on IVIg ($3500 every 2 weeks)
She was also an Astra Zeneca trial participant and her Vaccine Injury after the 1st dose was not reported in the trial data
https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.05.16.22274439v1?utm_source=substack&utm_medium=email
Excellent writeup here
Reduction in the infection fatality rate of Omicron variant compared with previous variants in South Africa
The reduction in the IFR of the Omicron variant was approximately 78.7% of the IFR of previous variants, with a 95% confidence interval (66.9%, 85.0%).
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9022446/#!po=1.35135
SARS-CoV-2 Omicron VOC Transmission in Danish Households
Omicron was 2.6–3.7 times more infectious than the Delta variant. However, they found no significant difference in transmissibility between the 2 variants in unvaccinated people.
https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.12.27.21268278v1
Amyloidogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein
https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.12.16.472920v1
The BNT162b2 mRNA SARS-CoV-2 vaccine induces transient afucosylated IgG1 in naive but not antigen-experienced vaccinees
[Afucosylated antibodies are recombinant monoclonal antibodieswith increased antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. The lack of fucose and not the presence of galactose is crucial for the ADCC effect. That is why it is called an ADCC antibody]
The findings reveal that the level of afucosylated anti-spike antibodies increases transiently in infection-naïve individuals after the first vaccine dose.
In infection-naïve individuals, about 25% of anti-spike IgG1 Fc were found to be afucosylated initially after administration of the first vaccine dose. However, the level decreased gradually with time.
In individuals with previous infection, about 2 – 10% of anti-spike IgG1 Fc were found to be afucosylated before vaccination. The level increased slightly after vaccination. The level of afucosylated anti-spike antibodies remained significantly lower in previously infected individuals after vaccination compared to that in naïve individuals
IgG lacking core fucosylation at this position initiates enhanced antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity by increased affinity to the Fc receptor FcRIIIa. Larsen et al.report that COVID-19 patients with severe symptoms have increased levels of anti–severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) IgG afucosylation compared with patients with mild disease.
Here, we report that afucosylated IgG (approximately 6% of total IgG in humans) are specifically formed against enveloped viruses but generally not against other antigens. This mediates stronger FcγRIIIa responses but also amplifies brewing cytokine storms and immune-mediated pathologies
The afucosylation of anti-S IgG may contribute to the exacerbation of COVID-19 in a subset of patients, resulting in ARDS. Thus, although they can be protective, antibodies potentially behave as double-edged swords and may contribute to the observed cytokine storm
https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.02.14.480353v1
Afucosylated IgG characterizes enveloped viral responses and correlates with COVID-19 severity
In accordance with our hypothesis and responses observed against other enveloped viruses, anti-S IgG responses against SARS-CoV-2 spike protein (S), which is expressed on the cell surface and the viral envelope, were strongly skewed toward low levels of core fucosylation. By contrast, re- sponses against the nucleocapsid protein (N) which is not expressed on the cell surface or viral envelope, were characterized by high lev- els of fucosylation (Fig. 3A). The IgG response appeared to be highly specific for SARS-CoV-2 because there was very weak or absent reactivity to SARS-CoV-2 antigens in pre-outbreak sam- ples, even to the more conserved N antigen (fig. S6) (22). The anti-S IgG1 responses of patients with ARDS recently (<5 days) hospitalized in intensive care units (ICUs) were significantly less fucosylated than in convalescent plasma donors consisting of individuals who were asymptomatic or had relative mild symptoms (non-ARDS) (Fig. 3A).
https://www.science.org/doi/pdf/10.1126/science.abc8378
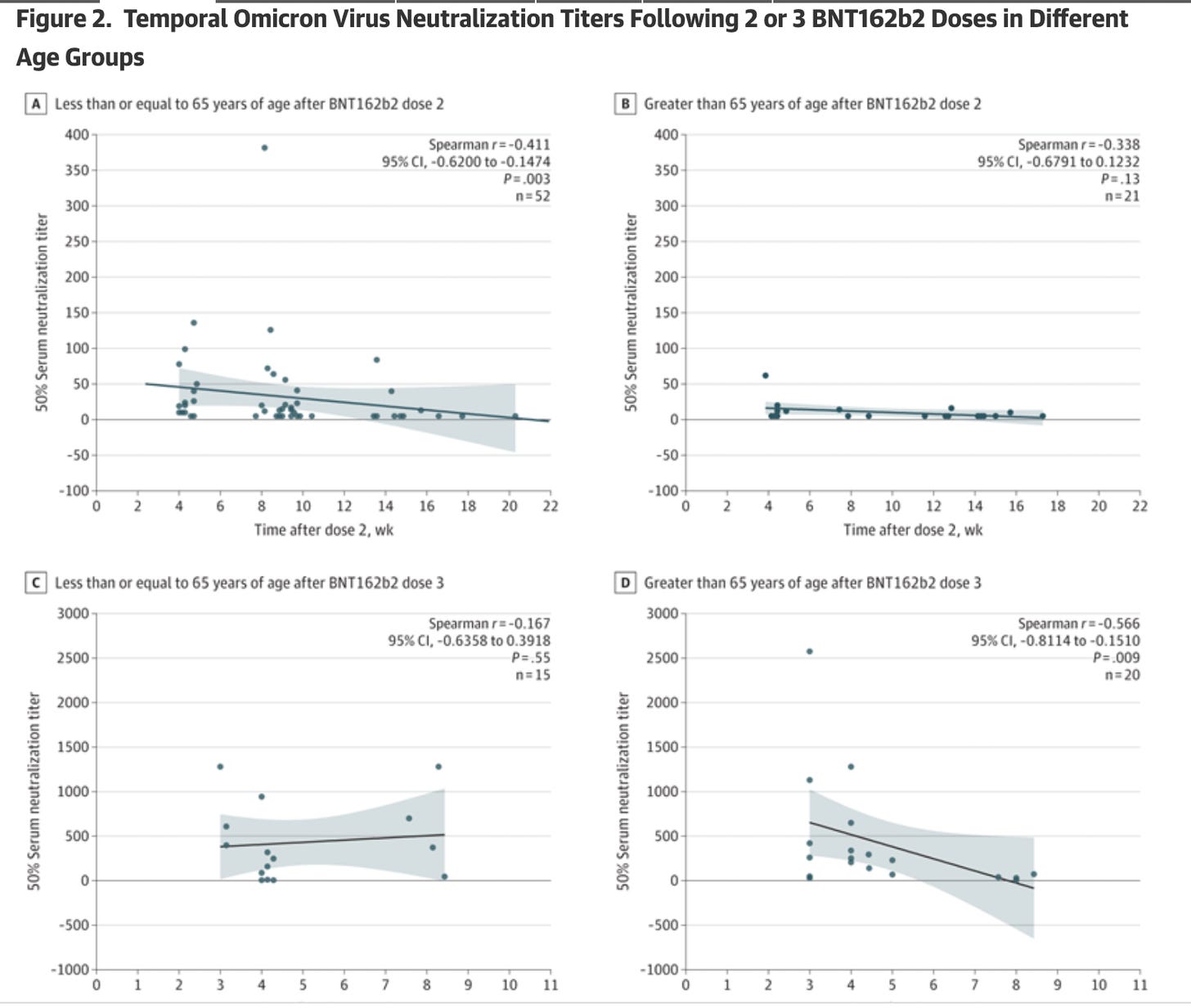
Neutralizing Antibodies Against the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant (BA.1) 1 to 18 Weeks After the Second and Third Doses of the BNT162b2 mRNA Vaccine. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5(5):e2212073. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.12073
This study detected a rapid decline in Omicron-specific serum neutralizing antibody titers only a few weeks after the second and third doses of BNT162b2.
For those aged 65 and older, there were almost no Omicron-specific serum neutralizing antibody titers after dose 2 (see Figure 2, panel B).
For those aged 65 and older, there were almost no Omicron-specific serum neutralizing antibody titers by week 8 after dose 3.
The article mentions that conserved T-cell immunity and non-neutralizing antibodies may still provide protection against hospitalization and death even as neutralizing antibodies wane, but the study did not actually measure T-cell immunity and non-neutralizing antibodies.
COVID-19: time from symptom onset until death in UK hospitalised patients
https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/928729/S0803_CO-CIN_-_Time_from_symptom_onset_until_death.pdf
Increased emergency cardiovascular events among under‐40 population in Israel during vaccine rollout and third COVID‐19 wave
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-022-10928-z.pdf
About 30% of COVID patients develop “Long COVID,” UCLA research finds
Itshould read 30% of hospitalized COVID patients
https://www.uclahealth.org/news/about-30-covid-patients-develop-long-covid-ucla-research
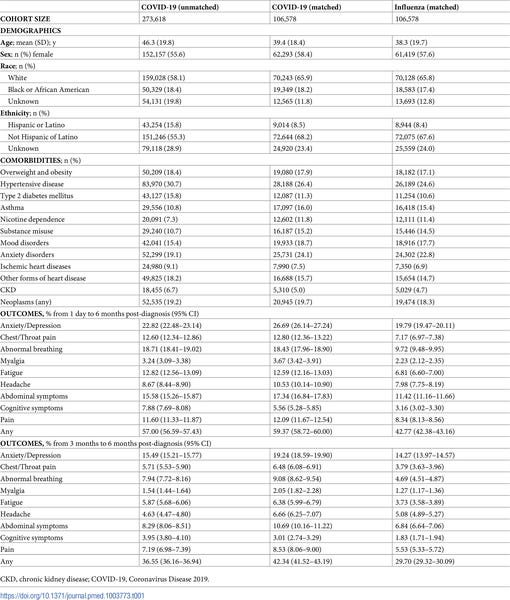
Incidence, co-occurrence, and evolution of long-COVID features: A 6-month retrospective cohort study of 273,618 survivors of COVID-19
9 core features of long-COVID (breathing difficulties/breathlessness, fatigue/malaise, chest/throat pain, headache, abdominal symptoms, myalgia, other pain, cognitive symptoms, and anxiety/depression)
36.55% between 3 and 6 months. The incidence of each feature was: abnormal breathing (7.94% ), fatigue/malaise (5.87%), chest/throat pain (5.71%), headache (4.63%), other pain (7.19%), abdominal symptoms (8.29%), myalgia (1.54%), cognitive symptoms (3.95%), and anxiety/depression (15.49%)
All 9 features were more frequently reported after COVID-19 than after influenza (with an overall excess incidence of 16.60% and hazard ratios between 1.44 and 2.04, all p< 0.001), co-occurred more commonly, and formed a more interconnected network.
Significant differences in incidence and co-occurrence were associated with sex, age, and illness severity.
Long-COVID clinical features occurred and co-occurred frequently and showed some specificity to COVID-19, though they were also observed after influenza
Most studies lack a control group and have limited generalizability, focusing either on hospitalized patients or individuals who voluntarily responded to a telephone survey or used an app.
https://journals.plos.org/plosmedicine/article?id=10.1371/journal.pmed.1003773
The Effectiveness of mRNA Vaccine Boosters for Laboratory-Confirmed COVID-19 During a Period of Predominance of the Omicron Variant of SARS-CoV-2
The estimated effectiveness (95% confidence interval) during days 7 to 34 after a booster was 51.3% (50.2, 52.4) overall
https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=4035396
Efficacy of a Fourth Dose of Covid-19 mRNA Vaccine against Omicron
Vaccine efficacy against any SARS-CoV-2 infection was 30% (95% confidence interval [CI], −9 to 55) for BNT162b2 and 11% (95% CI, −43 to 44) for mRNA-1273 (Figure 1C). Most infected health care workers reported negligible symptoms, both in the control group and the intervention groups. However, most of the infected participants were potentially infectious, with relatively high viral loads (nucleocapsid gene cycle threshold, ≤25)
https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMc2202542
Protection by a Fourth Dose of BNT162b2 against Omicron in Israel
Starting in the fifth week after the fourth dose, the rate ratio (RR) for infection began to fall. The adjusted rate of infection in the eighth week after the fourth dose was comparable to that of internal controls. The RR for the three-dose group relative to the four-dose group was 1.1, while the rate ratio for the internal control group, compared with the four-dose groups, was 1.0.
The RRs comparing controls with fourth-dose recipients were larger and lasted longer for severe disease. In the fourth week after the fourth dose, the adjusted rate of severe disease was lower by a factor of 3.5 than in three-dose recipients and a factor of 2.3 than in internal controls.
The adjusted rate of severe illness in the fourth week after the fourth dose was 1.6 cases per 100,000 person-days, compared with 5.5 cases per 100,000 in three-dose recipients and 3.6 cases per 100,000 in internal controls. The adjusted rate differences were 3.9 fewer cases per 100,000 person-days and 2.1 fewer cases per 100,000 than the three-dose group and internal controls, respectively.
Protection against confirmed infection appeared short-lived, whereas protection against severe illness did not wane during the study period (6 weeks)
https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa2201570
Estimating the effectiveness of the Pfizer COVID-19 BNT162b2 vaccine after a single dose.
After initial injection case numbers increased to day 8 before declining to low levels by day 21.
https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.02.01.21250957v1.full.pdf
Vaccination results in a rise in covid infection rates for the first week or two before there is a fall.
https://www.hartgroup.org/it-gets-worse-before-it-gets-better/
Sage-increased infection/hospitalization after vax
400% increase in symptomatic covid from before vaccination to the day of vaccination, in the hospitalised population. They say:
“We observed an abundance of patients admitted to hospital within 7 days of vaccination “.
A separate study from Brazil, later published in the Lancet, showed a 69% higher rate of covid in vaccinated healthcare workers (HCWs) compared to the unvaccinated in the first 13 days after vaccination.
https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanam/article/PIIS2667-193X(21)00017-X/fulltext#seccesectitle0017
Breakthrough infections with SARS-CoV-2 omicron despite mRNA vaccine booster dose
https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(22)00090-3/fulltext#sec1
Effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines against Omicron or Delta symptomatic infection and severe outcomes
In contrast to high levels of protection against both symptomatic infection and severe outcomes caused by Delta, our results suggest that 2 doses of COVID-19 vaccines only offer modest and short-term protection against symptomatic Omicron infection.
https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.12.30.21268565
Omicron: 3 vaccine doses are not enough to stop the new COVID variant, warns BioNTech CEO
Breakthrough infections with SARS-CoV-2 omicron despite mRNA vaccine booster dose
https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(22)00090-3/fulltext#sec1
High rate of BA.1, BA.1.1 and BA.2 infection in triple vaccinated
ConclusionWe report high incidence of omicron infections despite recent booster vaccination in triple vaccinated individuals. Vaccine-induced antibody titres seem to play a limited role in risk of omicron infection. High viral load and secretion of live virus for up to nine days may increase transmission in a triple vaccinated population.
.
Viral RNA trajectories were similar and suggestive of infectivity by all omicron sublineages, implying that three vaccine doses offer limited protection against BA.1, BA.1.1 and BA.2 infections and onward transmission.
Analysis of viral RNA levels revealed a peak day three after initial positive test, and that the majority (91%) of the participants were positive with Ct < 30 nine days after initial positive test.
23 of 61 (38%) participants remained asymptomatic > 48 hours after first qPCR-positive sample, with a median pre-symptomatic Ct value of 28.9 (range 19.4-38).
Six participants (9%) remained asymptomatic throughout the whose le course of their infection
Peak viral load and time to viral clearance was not significantly different between participants with asymptomatic course of infection and those with symptoms at any time point during the infection (p=0.06 and p=0.095, respectively).
Among the 55 participants with symptomatic infection (91%), “common cold” symptoms dominated.
Our findings emphasize that vaccine-induced antibody titres play a limited role in omicron infection risk prediction.
https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.04.02.22273333v1