CDC Setting Up Liability Waiver For Monkey Pox Treatments , COVID Vaccines “Potential” Impact on Monkey Pox Virulence and Setting the Stage to Bring Back Mass Small Pox Vaccination?
A brief note on Monkey Pox Treatment/Immunology
h/t Ryan Christian on The Last American Vagabond
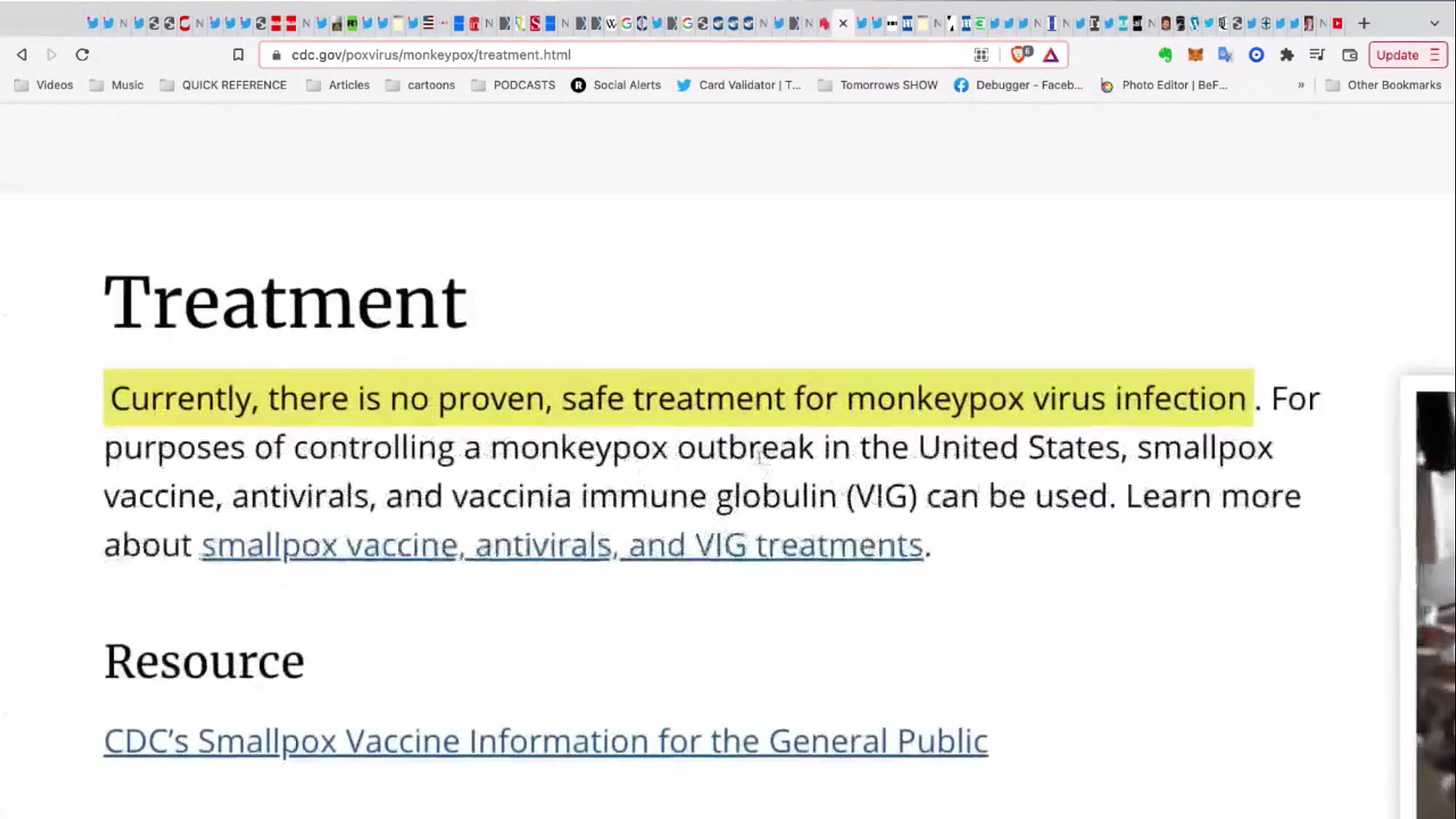
https://www.cdc.gov/poxvirus/monkeypox/treatment.html
This seems to lay the ground work for liability waiver for recently approved FDA drugs and vaccines for Small Pox
“At this time, there are no specific treatments available for monkeypox infection, but monkeypox outbreaks can be controlled.
One vaccine, JYNNEOSTM (also known as Imvamune or Imvanex), has been licensed in the United States to prevent monkeypox and smallpox. Because monkeypox virus is closely related to the virus that causes smallpox, smallpox vaccine can also protect people from getting monkeypox. Past data from Africa suggests that smallpox vaccine is at least 85% effective in preventing monkeypox
Data is not available on the effectiveness of Cidofovir and Brincidofovir in treating human cases of monkeypox. However, both have proven activity against poxviruses in in vitro and animal studies.
It is unknown whether or not a person with severe monkeypox infection will benefit from treatment with either antiviral, although their use may be considered in such instances. Brincidofovir may have an improved safety profile over Cidofovir”
https://www.cdc.gov/poxvirus/monkeypox/clinicians/treatment.htm
IMMUNOLOGY
“Monkey Pox has evolved several mechanisms to limit pathogenesis in the native host, including by increasing sensitivity to type I IFNs “
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4580173/
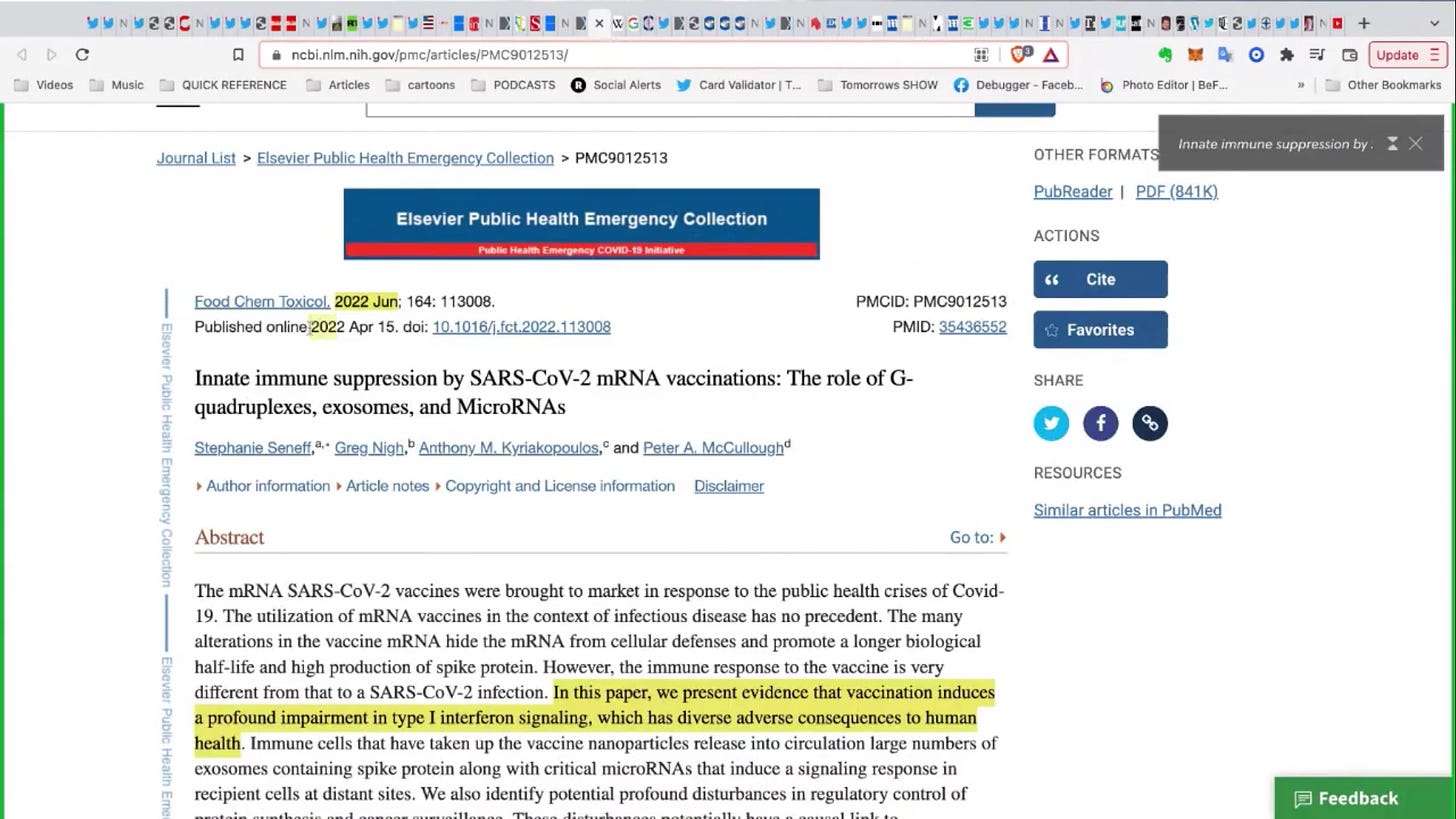
Innate Immune Suppression (Interferon I) in Vaccinated
“Type I interferons also play a central role in the pathogenesis and response against viral infections, including COVID-19 .
We observed a significant reduction in the production if IFN-α secreted after stimulation with poly I:C (TLR3 agonist) and R848 (TLR7/8 agonist) after the administration of the second dose of the vaccine .
This may hamper the initial innate immune response against the virus, as defects in TLR7 have been shown to result in and increased susceptibility to COVID-19 in young males
[Note-TLR3 is more important for Monkey Pox Virus since it is dsRNA and not ssRNA ]
These results collectively demonstrate that the effects of the BNT162b2 vaccine go beyond the adaptive immune system and can also modulate innate immune responses.”
https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.05.03.21256520v1
Innate Immune Suppression (Interferon I) in Vaccinated
Interferon I inhibits Monkey Pox Virus Replication
Published Study on February 11, 2022 appears to lay the ground work for a resumption of Smallpox Vaccinations to Curb Monkeypox threat
“It is plausible and logical that the increase in reported monkeypox cases is a consequence of increased population density, encroachment of human settlements into unknown animal reservoirs, or an increase in the population of susceptible individuals since the cessation of the smallpox vaccination programme. Almost all individuals under the age of 40 are unvaccinated in the DRC.[
The apparent increase in the average age of monkeypox cases in the DRC over time is likely to reflect the increase in the average age of susceptible individuals born after the discontinuation of smallpox vaccination, in 1980
While monkeypox virus has not established and propagated itself in the human population since the cessation of smallpox vaccination, the risks to populations in endemic areas are evident. “
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/pmid/31618206/